M. K. Jana, R. Song, H. Liu, D. R. Khanal, S. M. Janke, R. Zhao, C. Liu, Z. V. Vardeny, V. Blum, and D. B. Mitzi, Organic-to-inorganic structural chirality transfer in a 2D hybrid perovskite and impact on Rashba-Dresselhaus spin-orbit coupling., Nature Communications 11, 4699-1‑4699-10 (2020). doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18485-7.
S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: atomic structure Verified
See all entries for this property (2 total)
2D chiral perovksite
Origin: experimental (T = 298.0 K)
Space group: P 2₁
Crystal system: monoclinic
| a: | 8.7537 (±0.00019) Å |
| b: | 7.95502 (±0.00016) Å |
| c: | 19.5038 (±0.0005) Å |
| α: | 90° |
| β: | 93.806 (±0.002)° |
| γ: | 90° |
- temperature = 298.0 K
Sample type: single crystal
- data set 1629 (atomic structure)
- data set 1630 (band structure)
- data set 1864 (atomic structure)
- data set 2784 (circular dichroism (CD))
- data set 2785 (absorbance)
Starting materials: S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine, PbBr2
Product: S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide
Description: A hot solution of PbBr2 (45 mg, 0.12 mmol) and S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine (39 µL, 0.24 mmol ) in 0.5 ml aq. HBr and 1.2 ml deionized water in a sealed vial with an N2 atmosphere was slowly cooled from 95 °C to room temperature over 48 hr. The colorless, plate-like crystals were filtered, washed with diethyl ether, and vacuum-dried.
Method: Single crystal X-ray diffraction
Description: Single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed at 298 K on a Rigaku XtaLAB Synergy-S diffractometer using Mo-Kα radiation (λ=0.710 Å) and X-ray tube operating at 50 kV and 30 mA.
Entry added on: Aug. 4, 2020, 1:52 p.m.
Entry added by: Manoj Kumar Jana Duke University
Last updated on: Aug. 22, 2022, 3:22 p.m.
Last updated by: Rayan C Duke University
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
R-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: atomic structure Verified
See all entries for this property (2 total)
2D chiral perovskite
Origin: experimental (T = 298.0 K)
Space group: P 2₁
Crystal system: monoclinic
| a: | 8.75686 (±0.00018) Å |
| b: | 7.96109 (±0.00018) Å |
| c: | 19.5188 (±0.0006) Å |
| α: | 90° |
| β: | 93.773 (±0.002)° |
| γ: | 90° |
- temperature = 298.0 K
Sample type: single crystal
Starting materials: R-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine, PbBr2
Product: R-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide
Description: A hot solution of PbBr2 (45 mg, 0.12 mmol) and R-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine (39 µL, 0.24 mmol ) in 0.5 ml aq. HBr and 1.2 ml deionized water in a sealed vial with an N2 atmosphere was slowly cooled from 95 °C to room temperature over 48 hr. The colorless, plate-like crystals were filtered, washed with diethyl ether, and vacuum-dried.
Method: Single crystal X-ray diffraction
Description: Single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed at 298 K on a Rigaku XtaLAB Synergy-S diffractometer using Mo-Kα radiation (λ=0.710 Å) and X-ray tube operating at 50 kV and 30 mA.
Entry added on: Aug. 4, 2020, 1:58 p.m.
Entry added by: Manoj Kumar Jana Duke University
Last updated on: Aug. 22, 2022, 3:23 p.m.
Last updated by: Rayan C Duke University
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
S-1-methyl benzylamine lead iodide: atomic structure Verified
See all entries for this property (4 total)
2D chiral perovskite
Origin: experimental (T = 298.0 K)
Space group: P 2₁ 2₁ 2₁
Crystal system: orthorhombic
| a: | 8.9034 (±0.0002) Å |
| b: | 28.8647 (±0.0007) Å |
| c: | 9.3127 (±0.0002) Å |
| α: | 90° |
| β: | 90° |
| γ: | 90° |
- temperature = 298.0 K
Sample type: single crystal
Starting materials: (S)-(−)-α-methyl benzylamine, PbI2
Product: (S)-(−)-α-methyl benzylammonium lead iodide (S-MBA2PbI4)
Description: Single crystals of S-MBPI were grown by slowly evaporating a solution of (S)-(−)-α-methyl benzylamine (25 µL, 0.2 mmol) and PbI2 (45 mg, 0.1 mmol) in 1 ml aq. HI and 1 ml methanol at room temperature under N2 atmosphere. The orange-red, needle-like crystals were filtered, washed with diethyl ether, and vacuum-dried.
Method: Single crystal X-ray diffraction
Description: Single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed at 298 K on a Rigaku XtaLAB Synergy-S diffractometer using Mo-Kα radiation (λ=0.710 Å) and X-ray tube operating at 50 kV and 30 mA.
Entry added on: Aug. 4, 2020, 2:10 p.m.
Entry added by: Manoj Kumar Jana Duke University
Last updated on: Aug. 22, 2022, 3:26 p.m.
Last updated by: Rayan C Duke University
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
S-1-methyl benzylamine lead iodide: atomic structure Verified
See all entries for this property (4 total)
2D chiral perovskite
Origin: experimental (T = 200.0 K)
Space group: P 2₁ 2₁ 2₁
Crystal system: monoclinic
| a: | 8.8697 (±0.0002) Å |
| b: | 28.706 (±0.0008) Å |
| c: | 9.2496 (±0.0003) Å |
| α: | 90° |
| β: | 90° |
| γ: | 90° |
- temperature = 200.0 K
Sample type: single crystal
Starting materials: (S)-(−)-α-methyl benzylamine, PbI2
Product: (S)-(−)-α-methyl benzylammonium lead iodide (S-MBA2PbI4)
Description: Single crystals of S-MBPI were grown by slowly evaporating a solution of (S)-(−)-α-methyl benzylamine (25 µL, 0.2 mmol) and PbI2 (45 mg, 0.1 mmol) in 1 ml aq. HI and 1 ml methanol at room temperature under N2 atmosphere. The orange-red, needle-like crystals were filtered, washed with diethyl ether, and vacuum-dried.
Method: Single crystal X-ray diffraction
Description: Single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed at 200 K on a Rigaku XtaLAB Synergy-S diffractometer using Mo-Kα radiation (λ=0.710 Å) and X-ray tube operating at 50 kV and 30 mA.
Entry added on: Aug. 4, 2020, 2:14 p.m.
Entry added by: Manoj Kumar Jana Duke University
Last updated on: Aug. 22, 2022, 3:27 p.m.
Last updated by: Rayan C Duke University
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
S-1-methyl benzylamine lead iodide: atomic structure Verified
See all entries for this property (4 total)
2D chiral perovskite
Origin: experimental (T = 100.0 K)
Space group: P 2₁ 2₁ 2₁
Crystal system: orthorhombic
| a: | 28.6004 (±0.0006) Å |
| b: | 9.2078 (±0.0002) Å |
| c: | 8.84076 (±0.00019) Å |
| α: | 90° |
| β: | 90° |
| γ: | 90° |
- temperature = 100.0 K
Sample type: single crystal
Starting materials: (S)-(−)-α-methyl benzylamine, PbI2
Product: (S)-(−)-α-methyl benzylammonium lead iodide (S-MBA2PbI4)
Description: Single crystals of S-MBPI were grown by slowly evaporating a solution of (S)-(−)-α-methyl benzylamine (25 µL, 0.2 mmol) and PbI2 (45 mg, 0.1 mmol) in 1 ml aq. HI and 1 ml methanol at room temperature under N2 atmosphere. The orange-red, needle-like crystals were filtered, washed with diethyl ether, and vacuum-dried.
Method: Single crystal X-ray diffraction
Description: Single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed at 100 K on a Rigaku XtaLAB Synergy-S diffractometer using Mo-Kα radiation (λ=0.710 Å) and X-ray tube operating at 50 kV and 30 mA.
Entry added on: Aug. 4, 2020, 2:16 p.m.
Entry added by: Manoj Kumar Jana Duke University
Last updated on: Aug. 22, 2022, 3:29 p.m.
Last updated by: Rayan C Duke University
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: atomic structure Verified
See all entries for this property (3 total)
2D chiral perovskite
Origin: experimental (T = 298.0 K)
Space group: P 2₁
Crystal system: monoclinic
| a: | 19.2528 (±0.0009) Å |
| b: | 8.0769 (±0.0004) Å |
| c: | 8.728 (±0.0005) Å |
| α: | 90° |
| β: | 90.281 (±0.003)° |
| γ: | 90° |
- temperature = 298.0 K
Sample type: single crystal
Starting materials: 1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine (98%), PbBr2
Product: 1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammoium lead bromide
Description: A hot solution of 1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine (39 µL, 0.24 mmol ) and PbBr2 (45 mg, 0.12 mmol) in 0.5 ml of aq. HBr and 1.2 ml methanol is cooled from 95 °C to room temperature over 48 hr. The colorless plate-like crystals were filtered, washed with diethyl ether, and vacuum-dried.
Method: Single crystal X-ray diffraction
Description: Single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed at 298 K on a Bruker APEX II CCD diffractometer using Mo-Kα radiation (λ=0.710 Å) and X-ray tube operating at 50 kV and 30 mA
Entry added on: Aug. 4, 2020, 2:37 p.m.
Entry added by: Manoj Kumar Jana Duke University
Last updated on: Aug. 22, 2022, 3:31 p.m.
Last updated by: Rayan C Duke University
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead iodide: atomic structure Verified
chiral 1D lead iodide hybrid
Origin: experimental (T = 298.0 K)
Space group: P 2₁ 2₁ 2₁
Crystal system: orthorhombic
| a: | 8.1 (±0.0003) Å |
| b: | 8.4632 (±0.0003) Å |
| c: | 25.3124 (±0.0009) Å |
| α: | 90° |
| β: | 90° |
| γ: | 90° |
- temperature = 298.0 K
Sample type: single crystal
Starting materials: (S)-(−)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine (≥99%), PbI2
Product: S-NEA2Pb2I6 (S-NPI)
Description: Single crystals of 1D S-NEA2Pb2I6 (S-NPI) were obtained by cooling a hot aq. HI solution of S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine (0.25 mmol) and PbI2 (0.125 mmol) from 90 °C to room-temperature in 48 hr. The pale-yellow, needle-like crystals were filtered, washed with diethyl ether, and vacuum-dried.
Method: Single crystal X-ray diffraction
Description: Single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed at 298 K on a Bruker APEX II CCD diffractometer using Mo-Kα radiation (λ=0.710 Å) and X-ray tube operating at 50 kV and 30 mA
Entry added on: Aug. 4, 2020, 2:44 p.m.
Entry added by: Manoj Kumar Jana Duke University
Last updated on: Aug. 22, 2022, 3:32 p.m.
Last updated by: Rayan C Duke University
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: atomic structure Verified
See all entries for this property (3 total)
2D chiral perovskite
Origin: computational
Crystal system: triclinic
| a: | 19.281792 Å |
| b: | 7.89799713 Å |
| c: | 8.749358062 Å |
| α: | 90.00061278° |
| β: | 91.98100681° |
| γ: | 89.98667918° |
Sample type: single crystal
Code: FHI-aims
Level of theory: DFT
Exchange-correlation functional: PBE
K-point grid: 2×4×4
Level of relativity: atomic ZORA
Basis set definition: NAO
External repositories:
Entry added on: Aug. 11, 2020, 5:49 p.m.
Entry added by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Last updated on: Aug. 11, 2020, 5:49 p.m.
Last updated by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: atomic structure Verified
See all entries for this property (2 total)
2D chiral perovksite
Origin: computational
Crystal system: monoclinic
| a: | 19.26901142 Å |
| b: | 7.788285595 Å |
| c: | 8.763260853 Å |
| α: | 90.00049022° |
| β: | 95.33837551° |
| γ: | 89.9972677° |
Sample type: single crystal
- data set 1583 (atomic structure)
- data set 1630 (band structure)
- data set 1864 (atomic structure)
- data set 2784 (circular dichroism (CD))
- data set 2785 (absorbance)
Code: FHI-aims
Level of theory: DFT
Exchange-correlation functional: PBE
K-point grid: 2×4×4
Level of relativity: atomic ZORA
Basis set definition: NAO
External repositories:
Entry added on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:27 p.m.
Entry added by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Last updated on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:27 p.m.
Last updated by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: band structure Verified
2D chiral perovksite
Origin: computational
Crystal system: monoclinic


Sample type: single crystal
- data set 1583 (atomic structure)
- data set 1629 (atomic structure)
- data set 1864 (atomic structure)
- data set 2784 (circular dichroism (CD))
- data set 2785 (absorbance)
Code: FHI-aims
Level of theory: DFT
Exchange-correlation functional: HSE06
K-point grid: 3×4×4
Level of relativity: atomic ZORA with SOC
Basis set definition: NAO
Entry added on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:29 p.m.
Entry added by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Last updated on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:29 p.m.
Last updated by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
DOI for this data set: 10.6084/m9.figshare.12797465
Data set ID: 1630 Did you find any mistakes or inconsistencies about this data? Send us a note and we'll have a look at it and send you a reply. Thanks!R-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: atomic structure Verified
See all entries for this property (2 total)
2D chiral perovskite
Origin: computational
Crystal system: monoclinic
| a: | 19.2674511 Å |
| b: | 7.788913725 Å |
| c: | 8.763167748 Å |
| α: | 89.999996° |
| β: | 95.37403453° |
| γ: | 89.9995604° |
Sample type: single crystal
Code: FHI-aims
Level of theory: DFT
Exchange-correlation functional: PBE
K-point grid: 2×4×4
Level of relativity: atomic ZORA
Basis set definition: NAO
External repositories:
Entry added on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:32 p.m.
Entry added by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Last updated on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:32 p.m.
Last updated by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
R-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: band structure Verified
2D chiral perovskite
Origin: computational
Crystal system: monoclinic
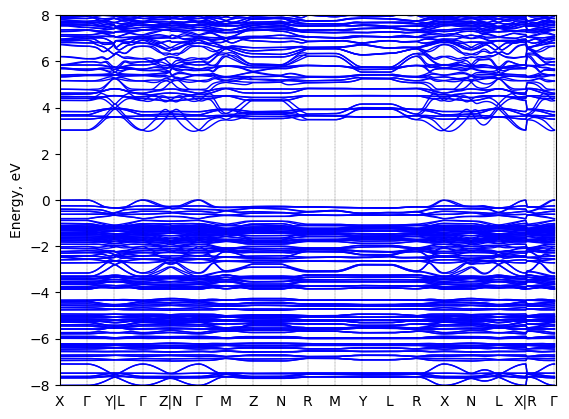
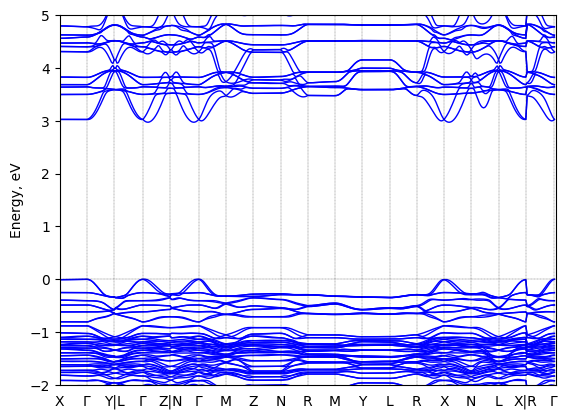
Sample type: single crystal
Code: FHI-aims
Level of theory: DFT
Exchange-correlation functional: HSE06
K-point grid: 3×4×4
Level of relativity: atomic ZORA with SOC
Basis set definition: NAO
Entry added on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:33 p.m.
Entry added by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Last updated on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:33 p.m.
Last updated by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
DOI for this data set: 10.6084/m9.figshare.12797483
Data set ID: 1632 Did you find any mistakes or inconsistencies about this data? Send us a note and we'll have a look at it and send you a reply. Thanks!1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: atomic structure Verified
See all entries for this property (3 total)
2D chiral perovskite
Origin: computational
Crystal system: monoclinic
| a: | 19.281792 Å |
| b: | 7.89799713 Å |
| c: | 8.749358062 Å |
| α: | 90.00061278° |
| β: | 91.98100681° |
| γ: | 89.98667918° |
Sample type: single crystal
Code: FHI-aims
Level of theory: DFT
Exchange-correlation functional: PBE
K-point grid: 2×4×4
Level of relativity: atomic ZORA
Basis set definition: NAO
External repositories:
Entry added on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:45 p.m.
Entry added by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Last updated on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:45 p.m.
Last updated by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: band structure Verified
2D chiral perovskite
Origin: computational
Crystal system: monoclinic
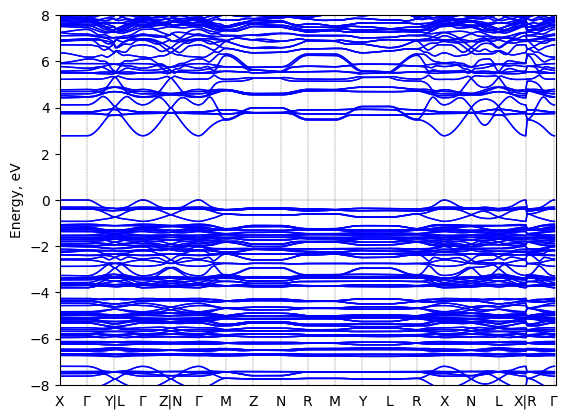
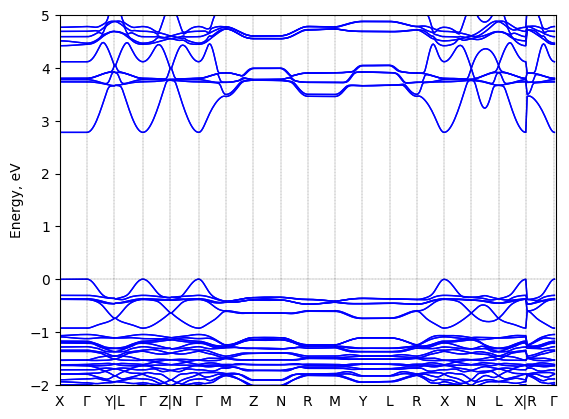
Sample type: single crystal
Code: FHI-aims
Level of theory: DFT
Exchange-correlation functional: HSE06
K-point grid: 3×4×4
Level of relativity: atomic ZORA with SOC
Basis set definition: NAO
Geometry used in the calculation
External repositories:
Entry added on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:47 p.m.
Entry added by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Last updated on: Sept. 16, 2022, 8:24 a.m.
Last updated by: Rayan C Duke University
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
DOI for this data set: 10.6084/m9.figshare.12797498
Data set ID: 1634 Did you find any mistakes or inconsistencies about this data? Send us a note and we'll have a look at it and send you a reply. Thanks!S-1-methyl benzylamine lead iodide: atomic structure Verified
See all entries for this property (4 total)
2D chiral perovskite
Origin: computational
Crystal system: orthorhombic
| a: | 28.82929846 Å |
| b: | 8.808198306 Å |
| c: | 9.185525184 Å |
| α: | 89.99937054° |
| β: | 89.97066632° |
| γ: | 90.01580536° |
Sample type: single crystal
Code: FHI-aims
Level of theory: DFT
Exchange-correlation functional: PBE
K-point grid: 2×4×4
Level of relativity: atomic ZORA
Basis set definition: NAO
External repositories:
Entry added on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:52 p.m.
Entry added by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Last updated on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:52 p.m.
Last updated by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
S-1-methyl benzylamine lead iodide: band structure Verified
2D chiral perovskite
Origin: computational
Crystal system: orthorhombic


Sample type: single crystal
Code: FHI-aims
Level of theory: DFT
Exchange-correlation functional: HSE06
K-point grid: 3×4×4
Level of relativity: atomic ZORA with SOC
Basis set definition: NAO
Geometry used in the calculation
External repositories:
Entry added on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:53 p.m.
Entry added by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Last updated on: Aug. 12, 2020, 2:53 p.m.
Last updated by: Ruyi Song Chemistry department, Duke university
Data correctness verified by:
- Rayan C Duke University
Download data
DOI for this data set: 10.6084/m9.figshare.12797519
Data set ID: 1636 Did you find any mistakes or inconsistencies about this data? Send us a note and we'll have a look at it and send you a reply. Thanks!S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: Band gap (fundamental, calculated) (DFT-HSE06+SOC)
2D chiral perovksite
Origin: computational
Crystal system: monoclinic
| Band gap (fundamental, calculated) (DFT-HSE06+SOC), eV |
|---|
Sample type: single crystal
Code: FHI-aims
Level of theory: DFT
Exchange-correlation functional: HSE06
K-point grid: 3×4×4
Level of relativity: atomic ZORA with SOC
Basis set definition: NAO
Entry added by: Rayan C Duke University
Last updated on: March 23, 2024, 12:48 a.m.
Last updated by: Rayan C Duke University
Download data
S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: thermal transition behavior
Origin: experimental
Sample type: unknown
Starting materials: (S)-(−)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine (>99%, Sigma Aldrich), lead bromide (PbBr2, 99.99%, TCI chemicals) , and hydrobromic acid (HBr) (48 wt% in H2O, >99.99%, Sigma Aldrich)
Product: [S-(−)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium]2PbBr4
Description: To grow S-NPB perovskite crystals, stoichiometric amounts of PbBr2 (90 mg, 0.24 mmol) and (S)-(−)-1- (1-naphthyl)ethylamine (78 µL, 0.48 mmol) were dissolved in aq. HBr (1.0 mL) and deionized water (2.4 mL) in a sealed vial at 95 °C. The hot solution was slowly cooled to room temperature (21 °C) over a period of 24 h in a water bath, resulting in the formation of colorless plate-like S-NPB single crystals.
Method: Thermal transition behavior
Description: DSC: Differential Scanning Calorimetry: DSC measurements were performed using a TA Discovery DSC instrument using various ramping rates and temperature ranges (as described in the main text) using a hermetically sealed aluminum pan and lid. Prior to experiments, the DSC setup was calibrated with metallic indium (melting temperature: 156.6 °C; enthalpy of melting: 28.71 J g−1), which upon repeating the experiment showed an acceptable temperature offset of 0.2 °C and melting enthalpy offset of 0.04%. Calibration and the above measurement were carried out at a ramp rate of 5 °C min−1. DSC analyses of crystalline S-NPB and rac-NPB perovskites were carried out by hermetically sealing corresponding crystals (≈5.0 mg) in aluminum pan/lid, and ramping temperature from 25 to 250 °C at a ramp rate of 5 °C min−1. For measurement of S-NPB and R-NPB glasses, samples were prepared by melting S-/R-NPB crystals (≈5.0 mg) in an open aluminum pan and quickly placing it on a metallic steel bench to quench to room temperature. After hermetic sealing, the glassy samples were exposed to a heating cycle with ramp rates of 5°C min−1 over a temperature range from 25 to 185 °C and heated isothermally at 185 °C for a minute, before cooling back to room temperature at ramp rates of 1, 5, and 20 °C min−1. Since the glass transition occurred over a temperature range, the Tg was determined using the midpoint halfheight method. The Tx, Tm, and Td temperatures were calculated using the intersection between the corresponding DSC peak onset with its horizontal baseline. For Tm, the onset temperature signifies the melting temperature of the sample under consideration, whereas the peak temperature corresponds to complete melting of the sample inside the apparatus. The enthalpy of crystallization and melting were calculated by measuring the area under the curve relating heat flow (W g−1)/ramp rate (°C s−1) and temperature. Thermogravimetric Analysis: TGA measurements were performed on a TA Q50 instrument using a 5 °C min−1 ramping rate from 25 to 300 °C under nitrogen gas flow (40 mL min−1) with samples (≈4.5 mg) of single crystals of S-NPB and rac-NPB perovskite. Glassy S-NPB perovskite sample (3.9 mg) for TGA measurement was prepared by scratching off the melt-quenched glass prepared on soda lime glass substrates
Entry added by: Chunyu Chen Mat. Sci Duke University
Last updated on: Dec. 8, 2024, 10:38 a.m.
Last updated by: Chunyu Chen Mat. Sci Duke University
Download data
S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: differential scanning calorimetry
Crystallization onset temperature (Beginning from glass) = 101.1 °C
Origin: experimental
Sample type: unknown
Starting materials: (S)-(−)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine (>99%, Sigma Aldrich), lead bromide (PbBr2, 99.99%, TCI chemicals) , and hydrobromic acid (HBr) (48 wt% in H2O, >99.99%, Sigma Aldrich)
Product: [S-(−)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium]2PbBr4
Description: To grow S-NPB perovskite crystals, stoichiometric amounts of PbBr2 (90 mg, 0.24 mmol) and (S)-(−)-1- (1-naphthyl)ethylamine (78 µL, 0.48 mmol) were dissolved in aq. HBr (1.0 mL) and deionized water (2.4 mL) in a sealed vial at 95 °C. The hot solution was slowly cooled to room temperature (21 °C) over a period of 24 h in a water bath, resulting in the formation of colorless plate-like S-NPB single crystals.
Method: Differential Scanning Calorimetry
Description: DSC: Differential Scanning Calorimetry: DSC measurements were performed using a TA Discovery DSC instrument using various ramping rates and temperature ranges (as described in the main text) using a hermetically sealed aluminum pan and lid. Prior to experiments, the DSC setup was calibrated with metallic indium (melting temperature: 156.6 °C; enthalpy of melting: 28.71 J g−1), which upon repeating the experiment showed an acceptable temperature offset of 0.2 °C and melting enthalpy offset of 0.04%. Calibration and the above measurement were carried out at a ramp rate of 5 °C min−1. DSC analyses of crystalline S-NPB and rac-NPB perovskites were carried out by hermetically sealing corresponding crystals (≈5.0 mg) in aluminum pan/lid, and ramping temperature from 25 to 250 °C at a ramp rate of 5 °C min−1. For measurement of S-NPB and R-NPB glasses, samples were prepared by melting S-/R-NPB crystals (≈5.0 mg) in an open aluminum pan and quickly placing it on a metallic steel bench to quench to room temperature. After hermetic sealing, the glassy samples were exposed to a heating cycle with ramp rates of 5°C min−1 over a temperature range from 25 to 185 °C and heated isothermally at 185 °C for a minute, before cooling back to room temperature at ramp rates of 1, 5, and 20 °C min−1. Since the glass transition occurred over a temperature range, the Tg was determined using the midpoint halfheight method. The Tx, Tm, and Td temperatures were calculated using the intersection between the corresponding DSC peak onset with its horizontal baseline. For Tm, the onset temperature signifies the melting temperature of the sample under consideration, whereas the peak temperature corresponds to complete melting of the sample inside the apparatus. The enthalpy of crystallization and melting were calculated by measuring the area under the curve relating heat flow (W g−1)/ramp rate (°C s−1) and temperature. Thermogravimetric Analysis: TGA measurements were performed on a TA Q50 instrument using a 5 °C min−1 ramping rate from 25 to 300 °C under nitrogen gas flow (40 mL min−1) with samples (≈4.5 mg) of single crystals of S-NPB and rac-NPB perovskite. Glassy S-NPB perovskite sample (3.9 mg) for TGA measurement was prepared by scratching off the melt-quenched glass prepared on soda lime glass substrates
Entry added by: Chunyu Chen Mat. Sci Duke University
Last updated on: Dec. 8, 2024, 10:38 a.m.
Last updated by: Chunyu Chen Mat. Sci Duke University
Download data
S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: Weight loss
Degradation onset temperature = 205.0 °C
Origin: experimental
Sample type: unknown
Starting materials: (S)-(−)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine (>99%, Sigma Aldrich), lead bromide (PbBr2, 99.99%, TCI chemicals) , and hydrobromic acid (HBr) (48 wt% in H2O, >99.99%, Sigma Aldrich)
Product: [S-(−)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium]2PbBr4
Description: To grow S-NPB perovskite crystals, stoichiometric amounts of PbBr2 (90 mg, 0.24 mmol) and (S)-(−)-1- (1-naphthyl)ethylamine (78 µL, 0.48 mmol) were dissolved in aq. HBr (1.0 mL) and deionized water (2.4 mL) in a sealed vial at 95 °C. The hot solution was slowly cooled to room temperature (21 °C) over a period of 24 h in a water bath, resulting in the formation of colorless plate-like S-NPB single crystals.
Method: Thermogravimetric Analysis
Description: Thermogravimetric Analysis: TGA measurements were performed on a TA Q50 instrument using a 5 °C min−1 ramping rate from 25 to 300 °C under nitrogen gas flow (40 mL min−1) with samples (≈4.5 mg) of single crystals of S-NPB and rac-NPB perovskite. Glassy S-NPB perovskite sample (3.9 mg) for TGA measurement was prepared by scratching off the melt-quenched glass prepared on soda lime glass substrates.
Entry added by: Chunyu Chen Mat. Sci Duke University
Last updated on: Dec. 8, 2024, 10:43 a.m.
Last updated by: Chunyu Chen Mat. Sci Duke University
Download data
S-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium lead bromide: Glass transition temperature
Glass transition temperature = 67.2 °C
Origin: experimental
Sample type: unknown
Starting materials: (S)-(−)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine (>99%, Sigma Aldrich), lead bromide (PbBr2, 99.99%, TCI chemicals) , and hydrobromic acid (HBr) (48 wt% in H2O, >99.99%, Sigma Aldrich)
Product: [S-(−)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylammonium]2PbBr4
Description: To grow S-NPB perovskite crystals, stoichiometric amounts of PbBr2 (90 mg, 0.24 mmol) and (S)-(−)-1- (1-naphthyl)ethylamine (78 µL, 0.48 mmol) were dissolved in aq. HBr (1.0 mL) and deionized water (2.4 mL) in a sealed vial at 95 °C. The hot solution was slowly cooled to room temperature (21 °C) over a period of 24 h in a water bath, resulting in the formation of colorless plate-like S-NPB single crystals.
Method: Glass transition temperature
Description: DSC: Differential Scanning Calorimetry: DSC measurements were performed using a TA Discovery DSC instrument using various ramping rates and temperature ranges (as described in the main text) using a hermetically sealed aluminum pan and lid. Prior to experiments, the DSC setup was calibrated with metallic indium (melting temperature: 156.6 °C; enthalpy of melting: 28.71 J g−1), which upon repeating the experiment showed an acceptable temperature offset of 0.2 °C and melting enthalpy offset of 0.04%. Calibration and the above measurement were carried out at a ramp rate of 5 °C min−1. DSC analyses of crystalline S-NPB and rac-NPB perovskites were carried out by hermetically sealing corresponding crystals (≈5.0 mg) in aluminum pan/lid, and ramping temperature from 25 to 250 °C at a ramp rate of 5 °C min−1. For measurement of S-NPB and R-NPB glasses, samples were prepared by melting S-/R-NPB crystals (≈5.0 mg) in an open aluminum pan and quickly placing it on a metallic steel bench to quench to room temperature. After hermetic sealing, the glassy samples were exposed to a heating cycle with ramp rates of 5°C min−1 over a temperature range from 25 to 185 °C and heated isothermally at 185 °C for a minute, before cooling back to room temperature at ramp rates of 1, 5, and 20 °C min−1. Since the glass transition occurred over a temperature range, the Tg was determined using the midpoint halfheight method. The Tx, Tm, and Td temperatures were calculated using the intersection between the corresponding DSC peak onset with its horizontal baseline. For Tm, the onset temperature signifies the melting temperature of the sample under consideration, whereas the peak temperature corresponds to complete melting of the sample inside the apparatus. The enthalpy of crystallization and melting were calculated by measuring the area under the curve relating heat flow (W g−1)/ramp rate (°C s−1) and temperature. Thermogravimetric Analysis: TGA measurements were performed on a TA Q50 instrument using a 5 °C min−1 ramping rate from 25 to 300 °C under nitrogen gas flow (40 mL min−1) with samples (≈4.5 mg) of single crystals of S-NPB and rac-NPB perovskite. Glassy S-NPB perovskite sample (3.9 mg) for TGA measurement was prepared by scratching off the melt-quenched glass prepared on soda lime glass substrates
Entry added by: Chunyu Chen Mat. Sci Duke University
Last updated on: Dec. 8, 2024, 10:45 a.m.
Last updated by: Chunyu Chen Mat. Sci Duke University
Download data